If you have diabetes, you might think bananas are too sweet to eat. I used to worry about this too. But here’s what I learned: bananas can be safe and healthy for people with diabetes when you eat them the right way.
Can People with Diabetes Eat Bananas?
Yes, most people with diabetes can eat bananas. This might surprise you.
The American Diabetes Association says that people with diabetes can enjoy fruit, including bananas. The key is eating them in the right amount and at the right time.
Bananas are real food with good nutrients. They’re not like candy or cake that only have sugar. When you eat a banana, you also get fiber, vitamins, and minerals that help your body.
What Makes Bananas Safe for Diabetics
Bananas have something special called fiber. A medium banana has about 3 grams of fiber.
Fiber helps slow down how fast sugar goes into your blood. Think of it like putting a speed bump on a road. The sugar can’t rush in all at once.
I remember when my friend Tom started checking his blood sugar after eating bananas. He was scared at first. But he noticed that when he ate a small banana with some peanut butter, his numbers stayed much better.
Bananas also have potassium. This mineral helps your heart stay healthy. People with diabetes need to take extra care of their hearts, so this is really helpful.
Understanding Banana Nutrition Facts
Let me break down what’s inside a medium banana:
A medium banana (about 126 grams) has 29 grams of carbohydrates and 112 calories. It has about 15 grams of sugar. The rest comes from starch and fiber.
But wait, there’s more good stuff. One banana gives you vitamin B6, which helps your brain work well. It also has magnesium and vitamin C.
The banana doesn’t have much fat or salt, which is great for people watching their health.
How Bananas Affect Blood Sugar Levels
This is what really matters, right? You want to know if a banana will make your blood sugar spike. Here’s the truth: bananas do raise blood sugar. But they don’t raise it as fast as white bread or candy.
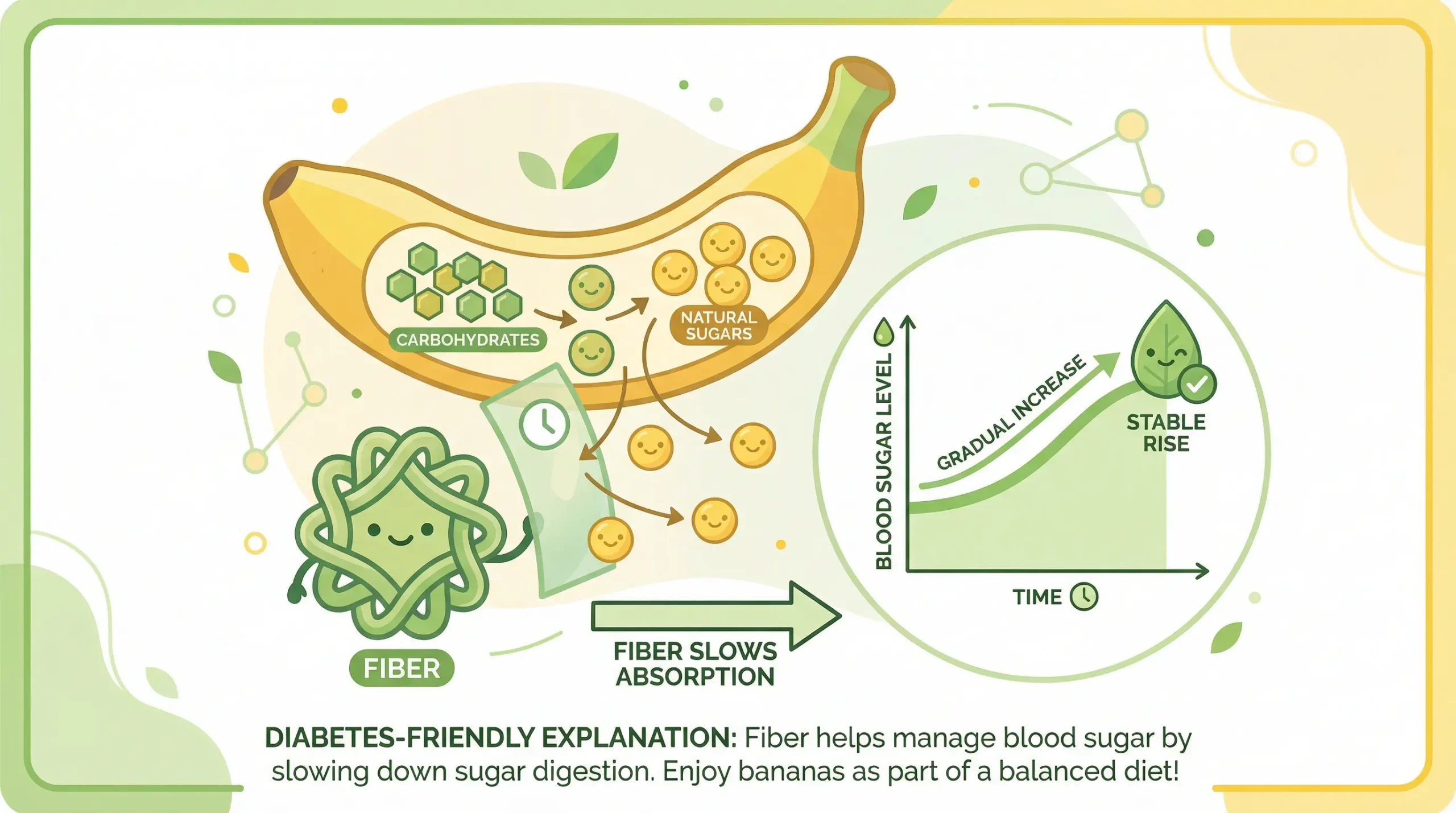
Carbohydrates and Natural Sugars in Bananas
All carbs raise your blood sugar. This includes the carbs in bananas.
When you eat a banana, your body breaks down the carbohydrates into sugar. This sugar goes into your blood. If you have diabetes, your body might not handle this sugar well.
But here’s what makes bananas different from a cookie. Bananas have natural sugars, not added sugar. Your body handles natural sugars better.
I talked to my doctor about this last year. She told me that the type of sugar matters just as much as the amount. Natural sugars from fruit come with fiber and nutrients. Added sugars in processed foods don’t.
The Role of Fiber in Blood Sugar Control
Fiber is like a helper in your body.
When you eat fiber with carbs, your body takes longer to break down the food. This means the sugar goes into your blood slowly instead of all at once.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, fiber helps people with diabetes manage their blood sugar better.
Think of it this way. If you pour water through a funnel, it flows slowly. If you pour water without a funnel, it splashes everywhere. Fiber works like a funnel for sugar.
A banana has both soluble fiber and insoluble fiber. The soluble fiber forms a gel in your stomach. This gel slows down how fast food moves through your body.
Glycemic Index and Glycemic Load of Bananas
Don’t worry, I’ll make this simple.
What Is Glycemic Index and Why Does It Matter
The glycemic index (or GI) is just a number. This number tells you how fast a food raises your blood sugar.
Foods with a low GI (55 or less) raise blood sugar slowly. Foods with a high GI (70 or more) raise it fast. Medium GI foods are between 56 and 69.
Bananas have a GI between 31 and 62. This means they’re in the low to medium range. The exact number depends on how ripe the banana is.
Studies from 2022 show that eating low GI foods helps people with type 2 diabetes keep their blood sugar steady.
How Banana Ripeness Changes GI
Here’s something cool I learned. The color of a banana changes how it affects your blood sugar.
A green (unripe) banana has a lower GI. It might be around 31 to 48. A yellow (ripe) banana has a higher GI, maybe 51 to 62. A brown (very ripe) banana has an even higher GI.
Why does this happen? As bananas get riper, the resistant starch inside them turns into regular sugar. The banana gets sweeter and raises blood sugar faster.
My neighbor Sarah learned this the hard way. She always ate very ripe bananas because she liked the sweet taste. Her blood sugar would go up more than she wanted. When she switched to bananas that were still a bit green, her numbers improved.
Health Benefits of Bananas for Diabetics
Bananas aren’t just safe. They can actually help your health in many ways.
Potassium and Heart Health
Potassium is a star player for your heart.
One medium banana has about 422 milligrams of potassium. Your body needs this mineral to keep your heart beating right and your blood pressure normal.
People with diabetes have a higher risk of heart disease. The National Institute of Diabetes says that keeping your heart healthy is really important when you have diabetes.
Research from 2022 found that people who eat bananas and other fruits regularly tend to have lower blood pressure. This can help protect your heart.
Potassium also helps balance the salt in your body. Too much salt can raise blood pressure. Potassium helps push out extra salt.
Resistant Starch and Blood Sugar Management
Now this part is interesting.
Resistant starch is a type of carb that your body can’t break down easily. It’s called “resistant” because it resists being turned into sugar.
Green bananas have lots of resistant starch. As the banana gets riper, it has less resistant starch and more regular sugar.
A study from 2023 tested 17 people with type 2 diabetes. They ate resistant starch from bananas. The results showed their fasting blood sugar went down. They also felt less hungry and fuller after eating.
This resistant starch also feeds the good bacteria in your gut. These bacteria help your body manage blood sugar better.
I started eating slightly green bananas after reading about this. I noticed I stayed full longer and didn’t get hungry between meals as much.
Best Ways to Eat Bananas with Diabetes
Knowing how to eat bananas makes all the difference.
Choosing the Right Banana Size and Ripeness
Size matters when it comes to bananas and diabetes.
A small banana (about 101 grams) has roughly 23 grams of carbs. A large banana (about 136 grams) has around 31 grams of carbs. An extra-large one can have up to 35 grams.
The bigger the banana, the more it will raise your blood sugar. Pick a smaller banana if you want to keep your carbs low.
For ripeness, go for bananas that are still firm. They should be yellow but not covered in brown spots. A few small brown spots are okay, but avoid bananas that are mostly brown.
Green bananas are even better. Yes, they’re less sweet. But they have more resistant starch and less sugar. Your blood sugar will thank you.
If you don’t like the taste of green bananas, try a banana that’s just starting to turn yellow. It’s a good middle ground.
Pairing Bananas with Protein and Healthy Fats
Never eat a banana alone. I mean it.
When you pair a banana with protein or healthy fats, your blood sugar stays steadier. The protein and fat slow down how fast the banana’s sugar gets into your blood.
Here are some good pairings I use:
- Banana with peanut butter (1 to 2 tablespoons). The healthy fats and protein in peanut butter balance out the carbs. Just make sure you use natural peanut butter without added sugar.
- Banana with Greek yogurt. Greek yogurt is high in protein. Add some banana slices to plain Greek yogurt. You can sprinkle a few nuts on top for extra crunch and healthy fat.
- Banana with nuts like almonds, walnuts, or pistachios. A small handful of nuts (about 10 to 15) works great. The combination keeps you full and prevents blood sugar spikes.
- Banana in a smoothie with protein powder. Blend a small banana with protein powder, some spinach, and unsweetened almond milk. This makes a filling drink that won’t spike your sugar too much.
My favorite is half a banana with almond butter. It’s simple, tastes great, and my blood sugar stays in a good range.
How Many Bananas Can a Diabetic Eat Per Day?
This is the question everyone asks.
Portion Control Tips
Most people with diabetes can safely eat one small to medium banana per day. But this depends on your personal situation.
Some people can eat one banana without problems. Others might need to stick to half a banana. It depends on your activity level, your medications, and how your body reacts.
Here’s a trick I learned. Cut your banana in half before you peel it. Eat one half now and save the other half for later. Cover the cut end with plastic wrap or stand it cut-side down on a plate to keep it fresh.
Don’t eat more than one banana at a time. Eating two or three bananas in one sitting gives you too many carbs all at once. Your blood sugar will likely go up too high.
Spread out your fruit during the day. If you eat half a banana at breakfast, you could have another fruit serving at lunch, like berries or an apple.
Tracking Your Carb Intake
You need to count banana carbs just like any other food.
If your doctor says you can have 45 grams of carbs at breakfast, and you eat a medium banana with 29 grams of carbs, you only have 16 grams left for other foods.
Keep a food diary or use an app. Write down what you eat and check your blood sugar two hours after eating. This shows you how the banana affects your personal numbers.
Everyone’s body is different. What works for your friend might not work for you. Testing your blood sugar helps you figure out the right amount for you.
My uncle has had diabetes for 15 years. He tests his blood sugar after every new food. He found out he can eat half a banana with breakfast, but a whole banana makes his sugar go too high. Your numbers might be different.
Green Bananas vs Ripe Bananas for Diabetes
Let’s dig deeper into this.
Why Unripe Bananas Are Better
Green bananas are the secret weapon for people with diabetes.
When a banana is green, it has lots of resistant starch. This starch doesn’t break down into sugar quickly. It moves through your stomach and small intestine without spiking your blood sugar.
A 2021 study looked at bananas at different ripeness levels. They found that as bananas ripen, the resistant starch decreases and the sugar increases. Green bananas had the most resistant starch.
This resistant starch also helps with weight control. It makes you feel full longer, so you eat less during the day. Many people with type 2 diabetes are trying to lose weight, so this is a big help.
I’ll be honest. Green bananas don’t taste as sweet. They’re a bit firmer and have a different texture. But if blood sugar control is your main goal, they’re worth trying.
You can cook green bananas too. In some countries, people boil or fry green bananas like you would a potato. They use them in savory dishes instead of sweet ones.
When to Avoid Overripe Bananas
Those brown, spotted bananas? Skip them if you have diabetes.
As a banana gets very ripe, almost all of the resistant starch turns into simple sugar. The glycemic index goes up. This means your blood sugar will rise faster.
Overripe bananas can taste great in banana bread or smoothies. But for someone with diabetes, they’re not the best choice.
If you buy bananas and they get too ripe before you eat them, you have two options. You can freeze them for later use in cooking. Or you can give them to someone without diabetes who can enjoy them.
My rule is simple: if the banana is more than 50% brown, I don’t eat it. I stick to yellow bananas with just a few brown spots or green bananas.
Common Mistakes When Eating Bananas with Diabetes
Let me save you from some trouble.
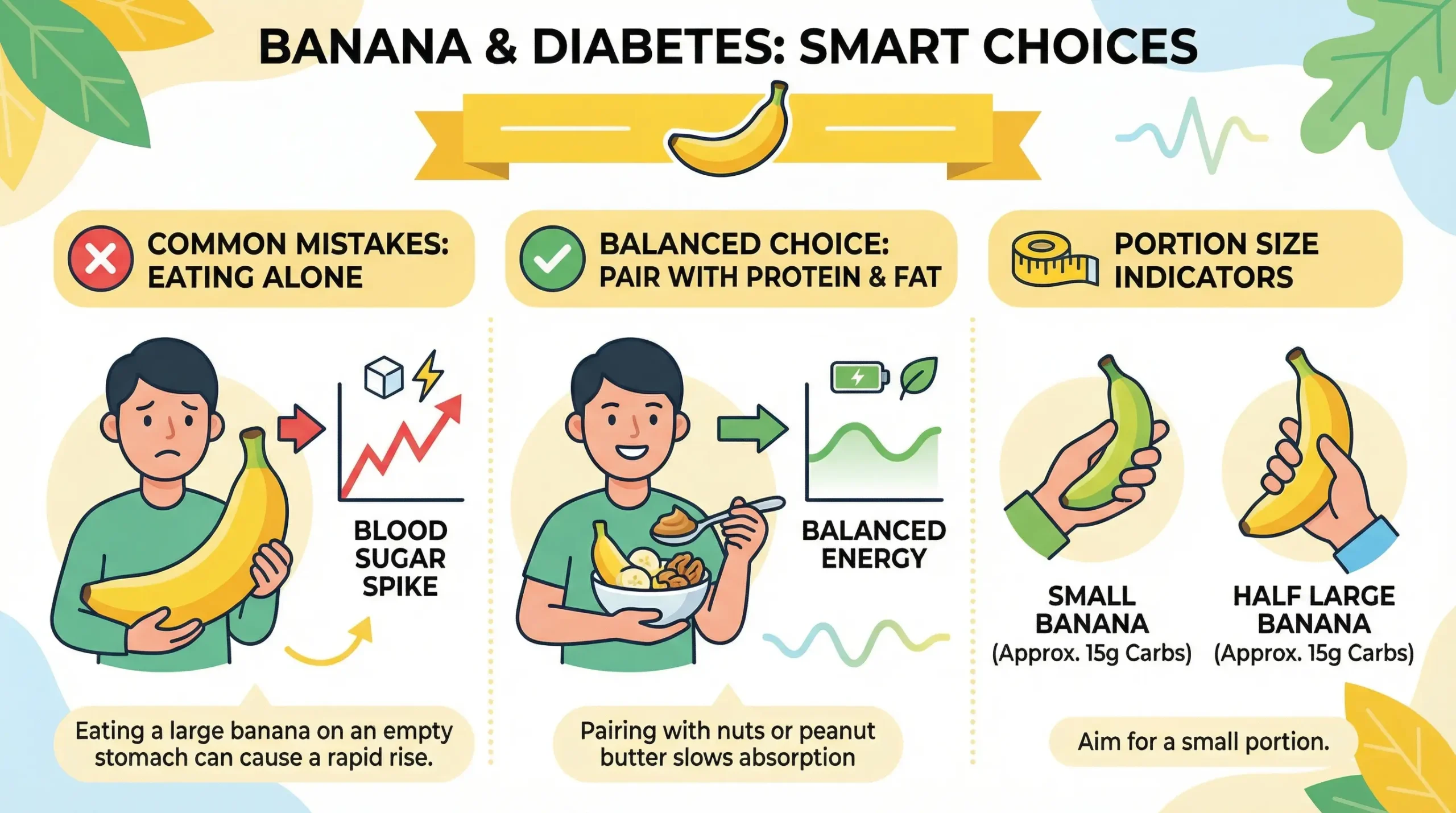
Eating Bananas Alone
This is mistake number one.
When you eat a banana by itself, all those carbohydrates hit your blood at once. There’s no protein or fat to slow things down.
Your blood sugar goes up faster and higher. Then it might drop too low later, making you feel tired and hungry again.
I made this mistake for years. I would grab a banana as a quick snack. My energy would spike for 30 minutes, then I’d feel exhausted. When I started adding peanut butter or eating the banana with eggs, everything changed. My energy stayed steady.
Always pair your banana with something that has protein or healthy fat. It doesn’t have to be fancy. Even a small handful of nuts works.
Ignoring Portion Sizes
Another big mistake is eating too much.
I’ve seen people eat two or three bananas after a workout, thinking it’s healthy. For someone with diabetes, that’s way too many carbs at once.
Even one large banana might be too much for some people. Start with a small banana or half of a medium one. Check your blood sugar. See how your body reacts.
Don’t guess. Measure and test. This is the only way to know what works for your body.
Some people also forget to count banana carbs in their total daily carb goal. If you eat a banana, those carbs count. You can’t eat all your regular foods and add a banana on top without affecting your blood sugar.
Conclusion
So, are bananas good for diabetics? Yes, they can be.
Bananas are a healthy fruit with fiber, potassium, and important vitamins. They can fit into your diet when you eat them the right way.
Choose smaller bananas that aren’t too ripe. Green or yellow bananas work better than brown ones. Always eat your banana with protein or healthy fats like peanut butter, Greek yogurt, or nuts.
Watch your portion sizes. Most people with diabetes can eat one small to medium banana per day. But check with your doctor or dietitian about what’s right for you.
Test your blood sugar after eating bananas. This helps you learn how your body reacts. Everyone is different, so your numbers might not match someone else’s.
Don’t be afraid of bananas. They’re not the enemy. With smart choices and portion control, you can enjoy this fruit and still manage your diabetes well.
Want more tips on living well with diabetes? Visit JustLiveWell.com for expert advice, healthy recipes, and practical guides to help you manage your health naturally and live your best life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do bananas raise blood sugar quickly?
Bananas raise blood sugar, but not as quickly as candy or white bread. They have a low to medium glycemic index (31 to 62). How fast they raise your blood sugar depends on the banana’s ripeness and what you eat with it. Green bananas raise blood sugar slower than very ripe ones. Eating a banana with protein or fat also slows down the blood sugar rise.
Can Type 2 diabetics eat bananas every day?
Many people with type 2 diabetes can eat one small to medium banana every day. But this depends on your personal carb limits, activity level, and blood sugar goals. Check with your doctor or dietitian. Test your blood sugar after eating bananas to see how your body reacts. Some people do fine with one banana daily, while others need to eat them less often or in smaller amounts.
Are green bananas better than yellow bananas for diabetes?
Yes, green bananas are usually better for people with diabetes. They have more resistant starch, which doesn’t raise blood sugar as much as regular sugar. As bananas ripen and turn yellow or brown, the resistant starch turns into sugar. This makes ripe bananas have a higher glycemic index. If you want better blood sugar control, choose green or slightly yellow bananas instead of very ripe ones.
What is the best time to eat a banana if you have diabetes?
The best time to eat a banana is with a meal or as a snack paired with protein or fat. Many people eat bananas at breakfast with eggs or Greek yogurt. Others have them as a snack with peanut butter or nuts. Avoid eating bananas late at night on an empty stomach, as this can cause blood sugar spikes while you sleep. The key is to never eat a banana alone and to space out your carbohydrate intake throughout the day.
Can bananas help lower blood pressure in diabetics?
Yes, bananas can help lower blood pressure because they’re high in potassium. One medium banana has about 422 milligrams of potassium. This mineral helps balance sodium levels and relax blood vessel walls, which can lower blood pressure. According to research, people who eat bananas and other fruits regularly tend to have lower blood pressure levels. This is especially helpful for people with diabetes, who often have high blood pressure. However, if you have chronic kidney disease or take certain blood pressure medications, talk to your doctor before eating lots of potassium-rich foods.


